Emergency Response Lacks Oxygen Solution
Brain damage occurs within minutes of breathing stopping. Presently, patients and victims have to wait until an Ambulance arrives to get the life saving oxygen they desperately need.
1. Medical Emergency
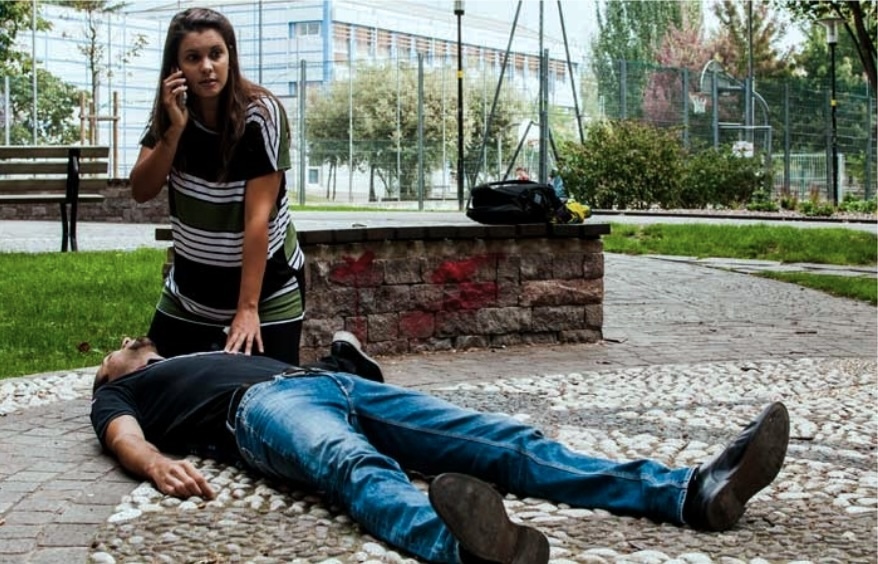

call for help
call for help
2. Initiate Response
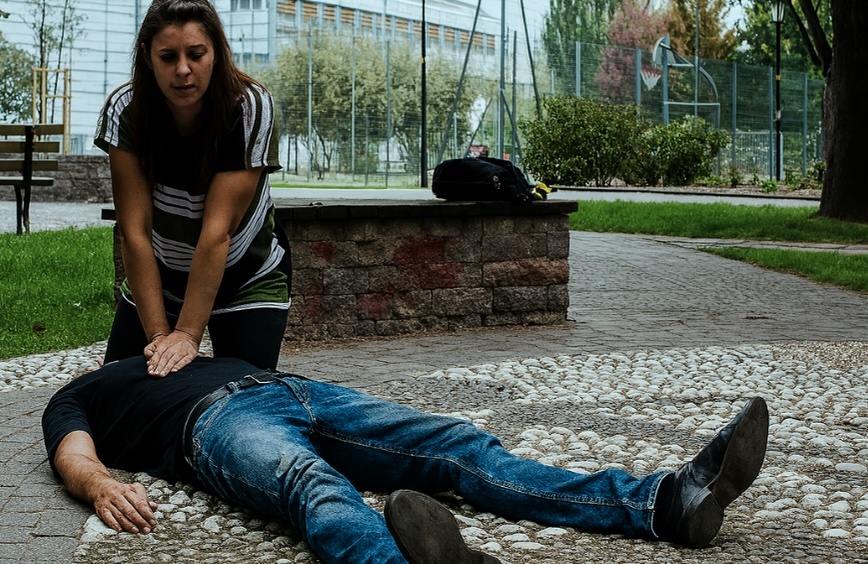


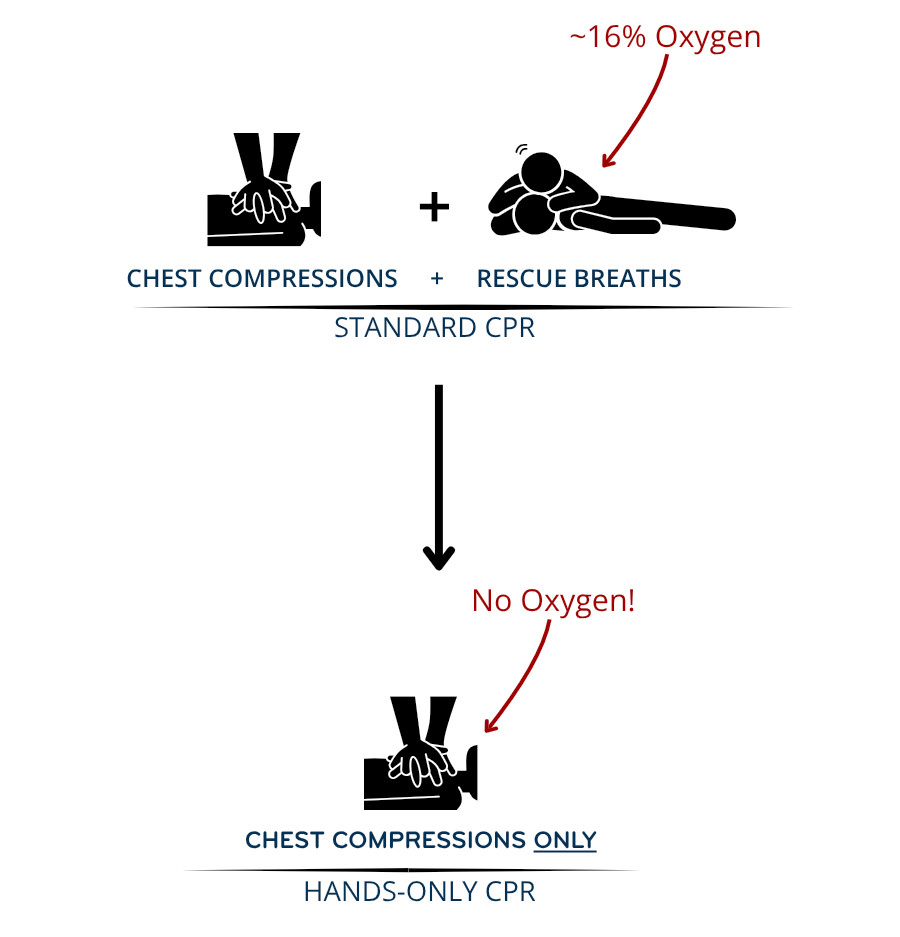
begin cpr without pulmonary RESUSCITATION oxygen

begin cpr without pulmonary RESUSCITATION oxygen
3. EMS Arrival


Continue cpr Until Help Arrives

Continue cpr Until Help Arrives
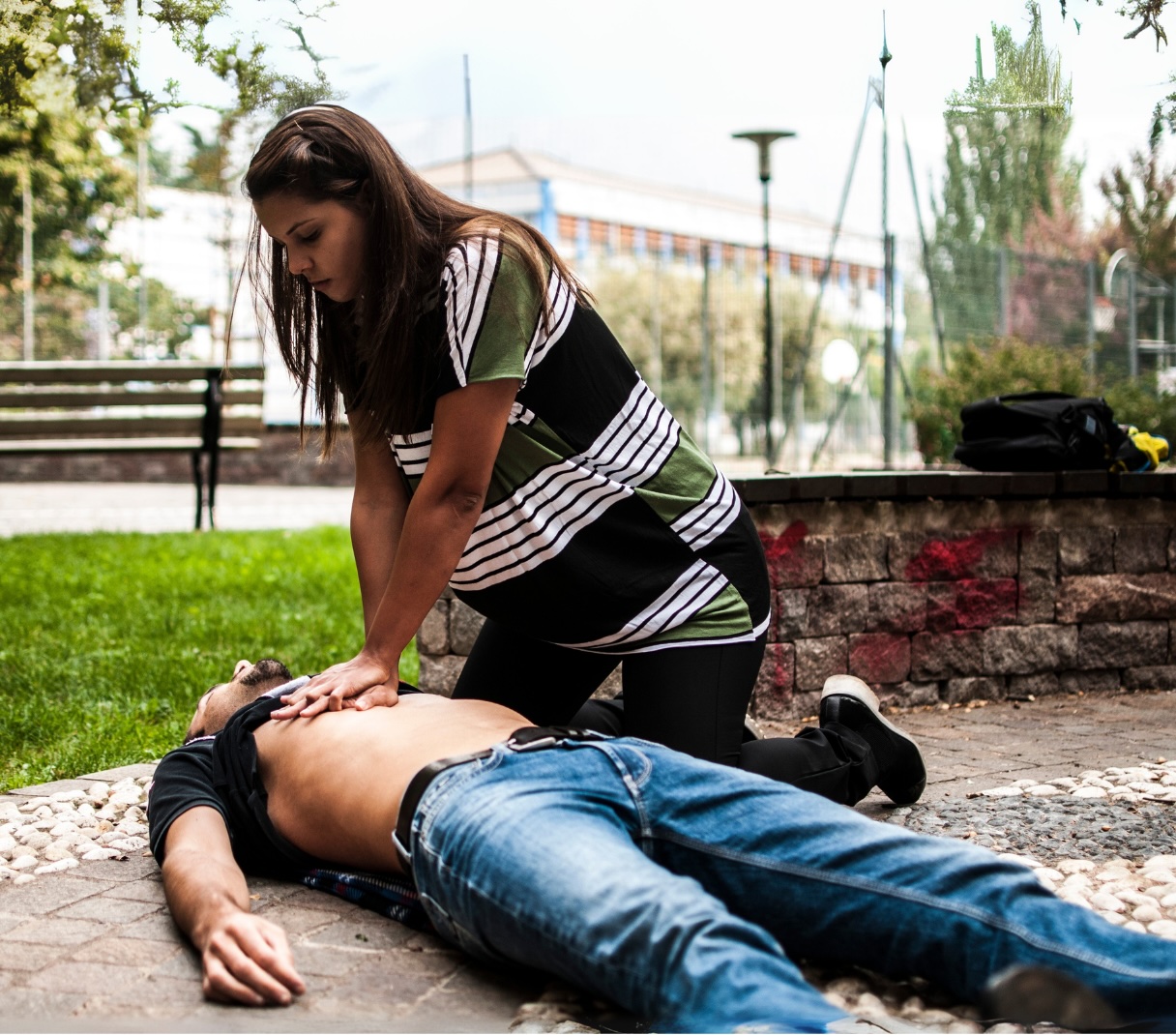

What are the Lay-Responder’s Options?

Bystander rescuers MAY give rescue breaths….BUT
- No longer recommended, unless the bystander is willing and able
- Exhaled air: 16% oxygen, over 100× more CO₂ than fresh air
- Potential fentanyl/opioid exposure risk
Where Hands-Only CPR Fails
- Respiratory emergencies: Opioid overdose, drowning, smoke inhalation
- Vulnerable populations: Children, pregnant individuals, older adults
- Chronic health risks: Obesity, smoking, lung disease
The AHA and ERC recommend providing rescue breaths during pediatric emergencies and suspected opioid overdoses, but only if the rescuer is willing and able to do so.
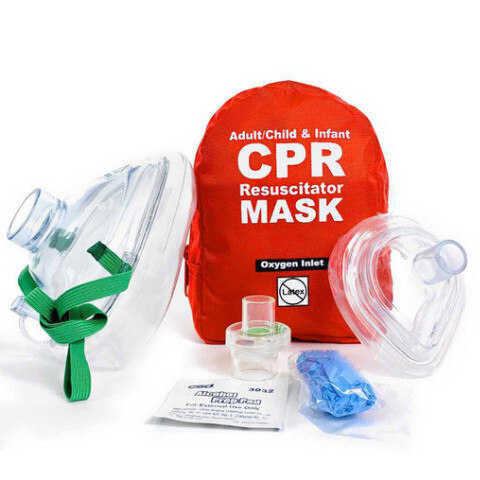
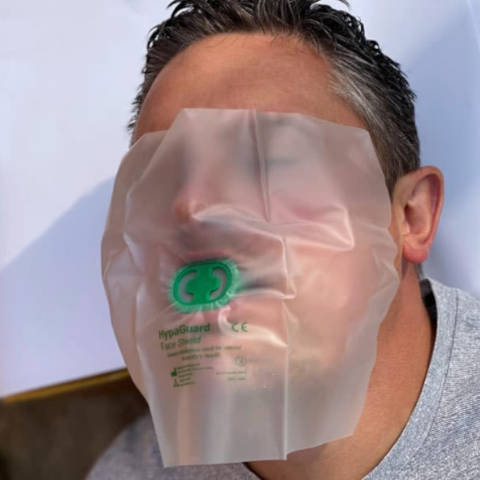
How Lay Responders Give Rescue Breaths Today
CPR Mask
Sheet Mask
- Exhaled air delivers only ~16% oxygen and over 100× more CO₂ than fresh air
- Masks are hard to seal, often leading to poor or failed ventilation
- Frequently skipped due to panic, lack of training, discomfort, or fear of infection (heightened post-COVID)